Fact Sheet: Biden-Harris Administration Announces Key AI Actions Following President Biden’s Landmark Executive Order
Three months ago, President Biden issued a landmark Executive Order to ensure that America leads the way in seizing the promise and managing the risks of artificial intelligence (AI). The Order directed sweeping action to strengthen AI safety and security, protect Americans’ privacy, advance equity and civil rights, stand up for consumers and workers, promote innovation and competition, advance American leadership around the world, and more.
Today, Deputy Chief of Staff Bruce Reed will convene the White House AI Council, consisting of top officials from a wide range of federal departments and agencies. Agencies reported that they have completed all of the 90-day actions tasked by the E.O. and advanced other vital directives that the Order tasked over a longer timeframe.
Taken together, these activities mark substantial progress in achieving the EO’s mandate to protect Americans from the potential risks of AI systems while catalyzing innovation in AI and beyond. Visit ai.gov to learn more.
Managing Risks to Safety and Security
The Executive Order directed a sweeping range of actions within 90 days to address some of AI’s biggest threats to safety and security. These included setting key disclosure requirements for developers of the most powerful systems, assessing AI’s risks for critical infrastructure, and hindering foreign actors’ efforts to develop AI for harmful purposes. To mitigate these and other risks, agencies have:
- Used Defense Production Act authorities to compel developers of the most powerful AI systems to report vital information, especially AI safety test results, to the Department of Commerce. These companies now must share this information on the most powerful AI systems, and they must likewise report large computing clusters able to train these systems.
- Proposed a draft rule that proposes to compel U.S. cloud companies that provide computing power for foreign AI training to report that they are doing so. The Department of Commerce’s proposal would, if finalized as proposed, require cloud providers to alert the government when foreign clients train the most powerful models, which could be used for malign activity.
- Completed risk assessments covering AI’s use in every critical infrastructure sector. Nine agencies—including the Department of Defense, the Department of Transportation, the Department of Treasury, and Department of Health and Human Services—submitted their risk assessments to the Department of Homeland Security. These assessments, which will be the basis for continued federal action, ensure that the United States is ahead of the curve in integrating AI safely into vital aspects of society, such as the electric grid.
Innovating AI for Good
To seize AI’s enormous promise and deepen the U.S. lead in AI innovation, President Biden’s Executive Order directed increased investment in AI innovation and new efforts to attract and train workers with AI expertise. Over the past 90 days, agencies have:
- Launched a pilot of the National AI Research Resource—catalyzing broad-based innovation, competition, and more equitable access to AI research. The pilot, managed by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), is the first step toward a national infrastructure for delivering computing power, data, software, access to open and proprietary AI models, and other AI training resources to researchers and students. These resources come from 11 federal-agency partners and more than 25 private sector, nonprofit, and philanthropic partners.
- Launched an AI Talent Surge to accelerate hiring AI professionals across the federal government, including through a large-scale hiring action for data scientists. TheAI and Tech Talent Task Force created by President Biden’s E.O. has spearheaded this hiring action and is coordinating other key initiatives to facilitate hiring AI talent. The Office of Personnel Management has granted flexible hiring authorities for federal agencies to hire AI talent, including direct hire authorities and excepted service authorities. Government-wide tech talent programs, including the Presidential Innovation Fellows, U.S. Digital Corps, and U.S. Digital Service, have scaled up hiring for AI talent in 2024 across high-priority AI projects. More information about the AI Talent Surge is available at ai.gov/apply.
- Began the EducateAI initiative to help fund educators creating high-quality, inclusive AI educational opportunities at the K-12 through undergraduate levels. The initiative’s launch helps fulfill the Executive Order’s charge for NSF to prioritize AI-related workforce development—essential for advancing future AI innovation and ensuring that all Americans can benefit from the opportunities that AI creates.
- Announced the funding of new Regional Innovation Engines (NSF Engines), including with a focus on advancing AI. For example, with an initial investment of $15 million over two years and up to $160 million over the next decade, the Piedmont Triad Regenerative Medicine Engine will tap the world’s largest regenerative medicine cluster to create and scale breakthrough clinical therapies, including by leveraging AI. The announcement supports the Executive Order’s directive for NSF to fund and launch AI-focused NSF Engines within 150 days.
- Established an AI Task Force at the Department of Health and Human Services to develop policies to provide regulatory clarity and catalyze AI innovation in health care. The Task Force will, for example, develop methods of evaluating AI-enabled tools and frameworks for AI’s use to advance drug development, bolster public health, and improve health care delivery. Already, the Task Force coordinated work to publish guiding principles for addressing racial biases in healthcare algorithms.
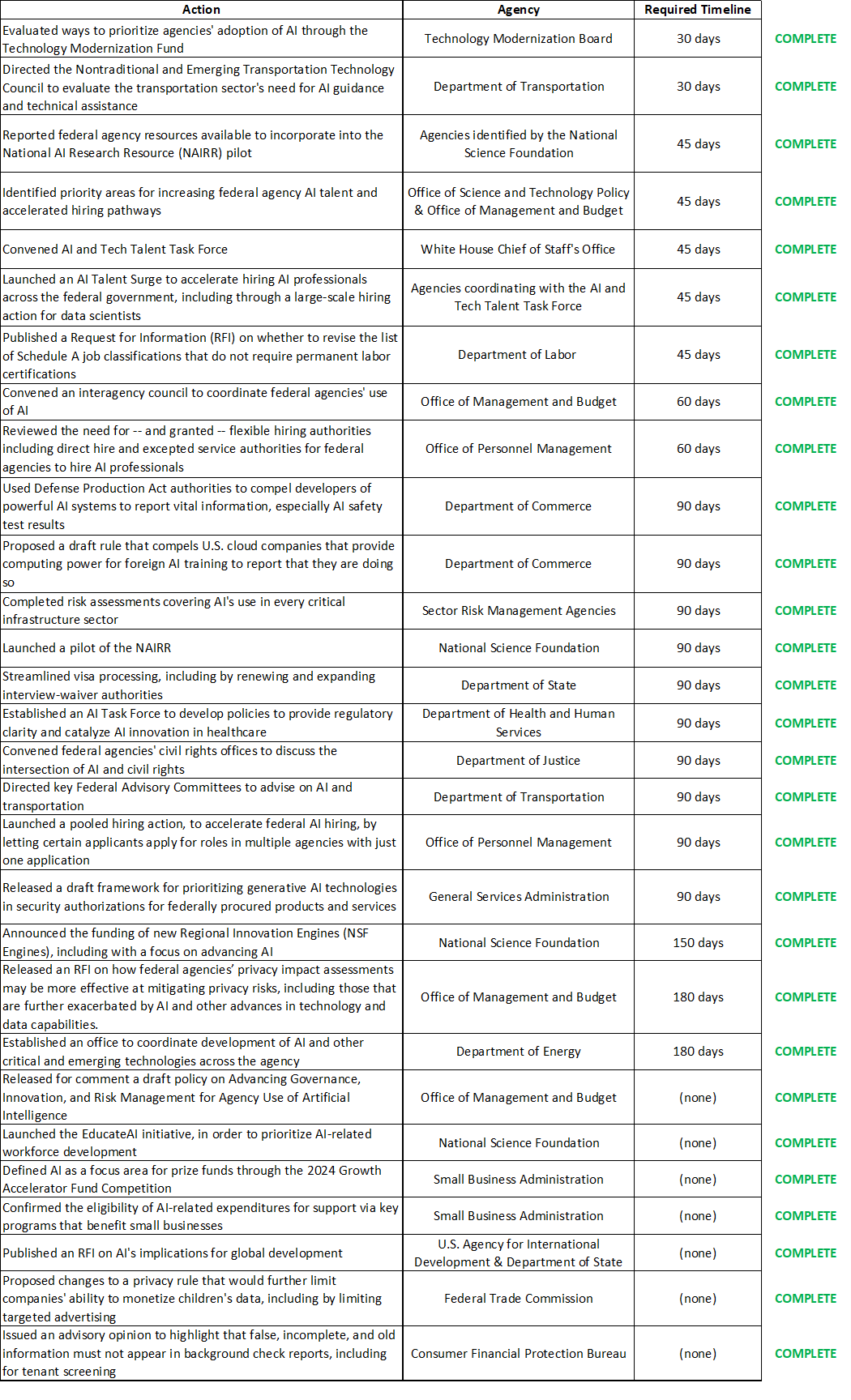
The table below summarizes many of the activities federal agencies have completed in response to the Executive Order.
###
